
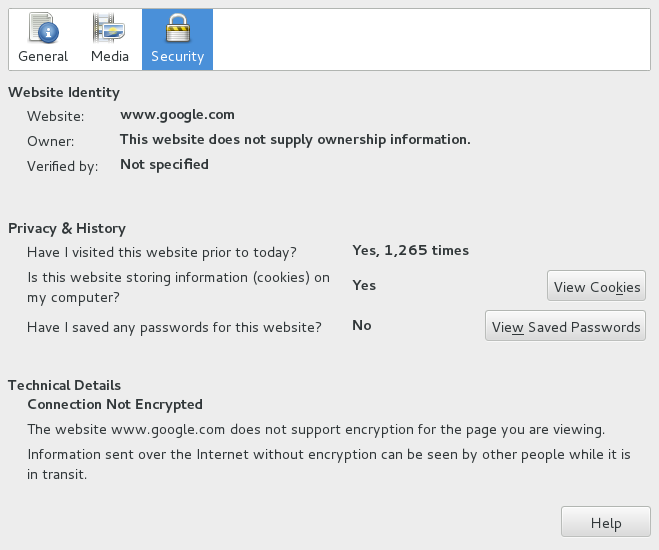
If you are the technical administrator or developer for your site, you should begin by assessing if you currently have any support for HTTPS.
YOUR CONNECTION IS NOT SECURE MOZILLA INSTALL
Using HTTPS requires that you obtain a TLS/SSL certificate(s), and then you can install that certificate and enable the HTTPS protocol on your web server. HTTPS uses the TLS/SSL protocol to provide a secure connection, which is both encrypted and authenticated. If you are seeing this warning on a site you own or operate, you should resolve it by enabling the HTTPS protocol for your site. The “Not Secure” warning is being displayed on any page served over HTTP, which is an insecure protocol. If you’re a visitor or an owner/operator of a website using HTTP and seeing this warning, here’s what you can do. Note that some websites may only support secure HTTPS connections on some pages, but not all in these cases, you may see the “Not Secure” warning on only the insecure pages. Over the last several years, websites have been transitioning to HTTPS - the S stands for “secure” - which does provide encryption and authentication and is used by millions of websites including Google, Facebook and Amazon, to protect your information while browsing, logging in and making purchases. Historically, this had been the primary protocol used for internet communication. Unsecure websites display the “Not Secure” warning which appears on all pages using the HTTP protocol, because it is incapable of providing a secure connection. Here’s what the “Not Secure” sign looks like in Chrome, Safari and Firefox. This article will cover what is behind the “Not Secure” warning and what site owners and visitors can do to fix it.įirst, note that the warning appears differently in different browsers. Website owners have a responsibility to secure their site, and although site visitors cannot change a “Not Secure” warning, they can request that site owners implement security measures. It only serves to alert you that you do not have a secure connection with that page.
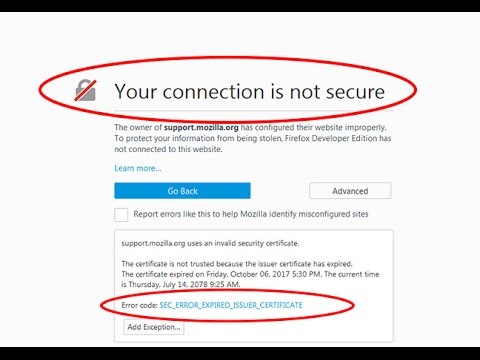
The “Not Secure” warning does not mean that your computer or the site you are visiting is affected by malware. It’s alerting you that information sent and received with that page is unprotected and it could potentially be stolen, read or modified by attackers, hackers and entities with access to internet infrastructure (like Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and governments). The “Not Secure” warning means there is a lack of security for the connection to that page. The latest version of Chrome also has a popup when you click the message that explains, “your connection to this site is not secure” and a warning about not entering any sensitive information on the site. Version 68 of the Google Chrome browser introduced a new “Not Secure” warning in the address bar that appears any time you are visiting an insecure web page.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
